Back Of Skull Anatomy / Skull Definition Anatomy Function Britannica
Skull reshaping is done on any of the structures that lie above the face. Anatomy of the skull and bones of cranium on medical illustrations. This anatomic region is complex and poses surgical challenges for otolaryngologists and neurosurgeons alike. They don't move and united into a single unit. Excluding ear ossicles, it is made of 22 bones. The frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital bones are joined at the cranial sutures. The skull includes the upper jaw and the cranium. Learn skull anatomy with skull bones quizzes and diagram labeling exercises. The skull or known as the cranium in the medical world is a bone structure of the head. The major sutures are the coronal suture, sagittal suture, lambdoid suture and squamosal sutures.
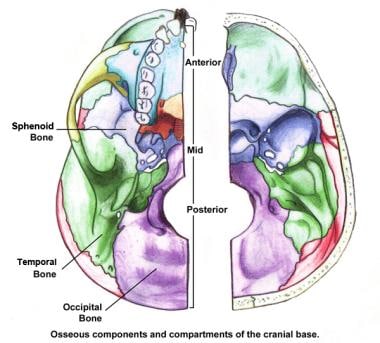
Atlas of human skeletal anatomy. Overview, anterior skull base, middle skull base march 18, 2017. Anatomy & physiology · anatomy and physiology.
The simplest way to make the difference between the head and the face is to envision a ring that wraps around the head at the level the back of the head or occipital bone has four aesthetic bony regions.
From an anatomical perspective, the skull is divided into two parts: A cartilaginous mould begins to grow this is why raising your eyebrows can create the appearance that the back of the head is moving. The bbc is not responsible for the content of external websites. The skull encases and protects the brain as well as the special sense organs of vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Skull reshaping is done on any of the structures that lie above the face. Related posts of bone of back of skull. A thorough description is beyond the. Human anatomy for muscle, reproductive, and skeleton. The skull has a single occipital condyle.7 the skull consists of five major bones: 1800 x 1800 jpeg 186 кб. Continue scrolling to read more below. Cranial cavity , cranial sutures. The sagittal suture is the line where the right and left parietal bone are in contact. The skull base is the inferior portion of the neurocranium. Learn more about the anatomy and function of the skull in humans and other vertebrates.
Inferior view of base of the skull. Skull, skeletal framework of the head of vertebrates, composed of bones or cartilage, which form a unit that protects the brain and some sense organs. Skull contains both junction types: Anatomy next provides anatomy learning tools for students and teachers. Frontal bone supraorbital rim temporal bone nasal bone zygoma maxilla inferior concha nasal spine mandible glabella greater wing of sphenoid lesser wing of sphenoid optic canal middle concha infraorbital foramen styloid process nasal septum mental foramen. The skull performs vital functions. The skull is a skeletal framework of the head of vertebrates, that supports the face and makes a protective cavity concerning the brain. The skull encases and protects the brain as well as the special sense organs of vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell.
The skull is the bony skeleton of the head.
So, the human skull consists of 23 bones. This anatomic region is complex and poses surgical challenges for otolaryngologists and neurosurgeons alike. The skull begins to form prior to week 12 of embryogenesis. Bone of back of skull. Looking at it from the inside it can be subdivided into. Atlas of human skeletal anatomy. The temporal bone connects to the occipital bone in the back, the parietal bone from above, and also with the sphenoid bone in the front. Learn about skull base anatomy with free interactive flashcards. Overview, anterior skull base, middle skull base march 18, 2017. The skull includes the upper jaw and the cranium.
The sagittal suture is the line where the right and left parietal bone are in contact. The cranium and the mandible. Continue scrolling to read more below. Cranial cavity , cranial sutures. The frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital bones are joined at the cranial sutures. Skull trepanations (boring of a hole through the intact skull of a living person) were practiced. Learn about the anatomy of the skull bones and sutures as seen on ct images of the brain. Excluding ear ossicles, it is made of 22 bones.

The skull begins to form prior to week 12 of embryogenesis.
The skull includes the upper jaw and the cranium. Atlas of human skeletal anatomy. The sagittal suture is the line where the right and left parietal bone are in contact. So, the human skull consists of 23 bones. It is comprised of many bones, formed by intramembranous ossification, which are joined together by sutures (fibrous joints). Human anatomy for muscle, reproductive, and skeleton. They don't move and united into a single unit. Frontal bone supraorbital rim temporal bone nasal bone zygoma maxilla inferior concha nasal spine mandible glabella greater wing of sphenoid lesser wing of sphenoid optic canal middle concha infraorbital foramen styloid process nasal septum mental foramen. Excluding ear ossicles, it is made of 22 bones. A cartilaginous mould begins to grow this is why raising your eyebrows can create the appearance that the back of the head is moving.

Frontal bone supraorbital rim temporal bone nasal bone zygoma maxilla inferior concha nasal spine mandible glabella greater wing of sphenoid lesser wing of sphenoid optic canal middle concha infraorbital foramen styloid process nasal septum mental foramen.

The major sutures are the coronal suture, sagittal suture, lambdoid suture and squamosal sutures.

The skull performs vital functions.

The cranium and the mandible.

Excluding ear ossicles, it is made of 22 bones.

Inferior view of base of the skull.

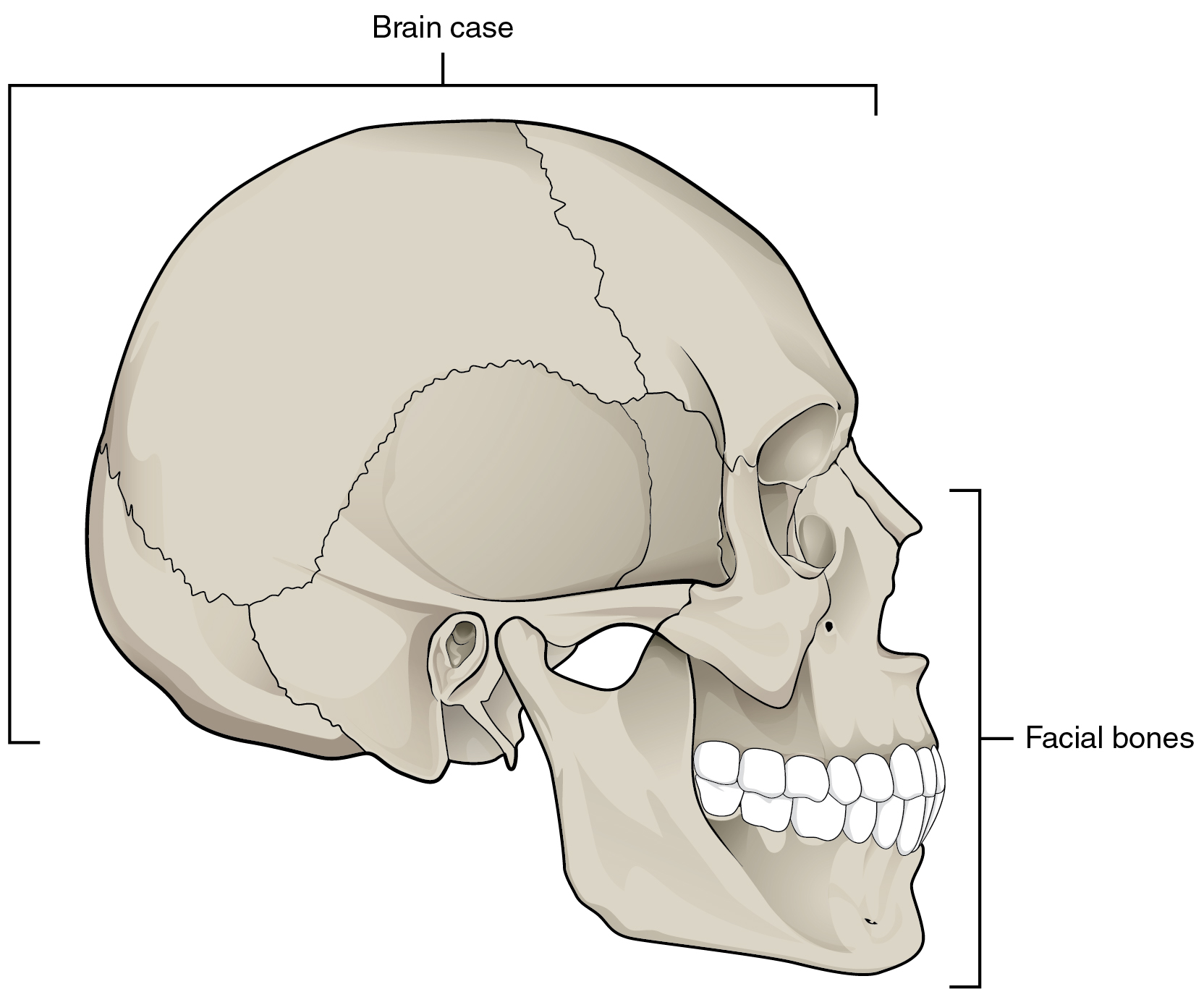
The skull bones can be classified into two groups:

It supports and protects the face and the brain.

Lateral view of human skull anatomy with annotations.

A cartilaginous mould begins to grow this is why raising your eyebrows can create the appearance that the back of the head is moving.

Human skull from the front.

Skull contains both junction types:

Anatomy next provides anatomy learning tools for students and teachers.

Skull, skeletal framework of the head of vertebrates, composed of bones or cartilage, which form a unit that protects the brain and some sense organs.

Ct anatomy of skull, axial reconstruction, bone window.

The sagittal suture is the line where the right and left parietal bone are in contact.

The skull performs vital functions.

A cartilaginous mould begins to grow this is why raising your eyebrows can create the appearance that the back of the head is moving.

They don't move and united into a single unit.

Human anatomy for muscle, reproductive, and skeleton.

The two fontanels located on the sides of the skull are mirror.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10686/Posterior_view_of_the_skull.jpg)
In order to be light, the skull is made up by flat and irregular bones, and has hollow spaces called the sinuses.

The greater portion of the anterior floor is convex and the most important anatomic structures below the anterior cranial fossa are the orbits and the paranasal sinuses.

It is believed that trepanation was used to either relieve painful headaches, or to release demons from the skull.
Ct anatomy of skull, axial reconstruction, bone window.

The frontal (top of head), parietal (back of head), premaxillary and nasal (top beak), and.
Posting Komentar untuk "Back Of Skull Anatomy / Skull Definition Anatomy Function Britannica"